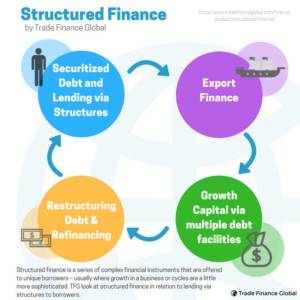
Structured Finance
Structured Finance is a complex form of financing, usually used on a scale too large for an ordinary loan or bond. Collateralized debt-obligations, syndicated loans and Mortgage-Backed Securities – the C4 behind the 2008 financial crisis – are all examples of Structured Finance.
When it comes to financing a transaction, there are ‘normal’ or ‘vanilla’ types of financial instruments widely available on the market. These are instruments such as a mortgages or overdrafts and look at the credit strength of the borrower.
However, there are borrowers in the market with unique requirements. With unique borrowers, comes a unique financing instrument. Structured finance refers to an instrument which helps dampen risk when applied to securitizations of various assets.
It is often perceived as the packaging up of receivables, however when we usually look at structured finance it is in relation to lending to borrowers through structures, and less about focusing on the packaging of debt.
The aim is to create situations in order to provide non-flow financing solutions and structured risk mitigation products for clients when looking at a number of industries and classes of assets.
Why is Structured Finance important?
One reason behind Structured Finance’s importance is because of the parties involved. Large institutions such as Banks participate in the use of structured finance, which means the sums that are made available and circulating the economy through the process are massive.
An example – if we mute the effects that the 2008 financial crisis had on the world, we can see that mortgage-backed securities were bought by the Federal Reserve for roughly $38billion. Consequently, through no fault of the basic concept, MBS’s crippled the American economy along with many others however it also (to begin with) generated large surpluses of money.
Why would you use structured finance?
Structured finance can aid companies restructure debt, make savings on repayments, and free up working capital to make cash work as efficiently as it can do. Furthermore, it is often useful when a company operates in different jurisdictions and trades globally.
 Australia
Australia Hong Kong
Hong Kong Japan
Japan Singapore
Singapore United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates United States
United States France
France Germany
Germany Ireland
Ireland Netherlands
Netherlands United Kingdom
United Kingdom