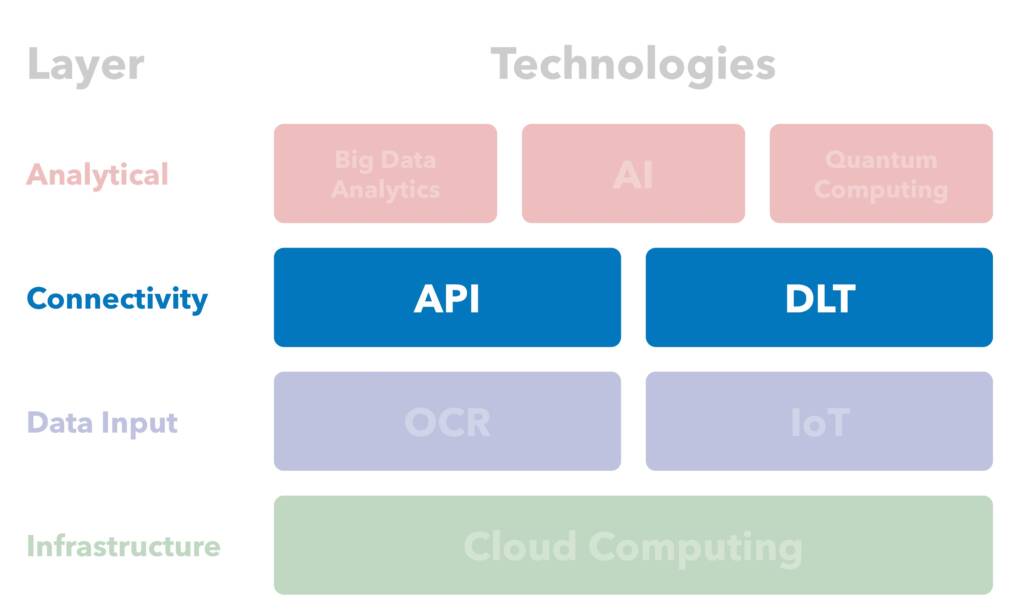
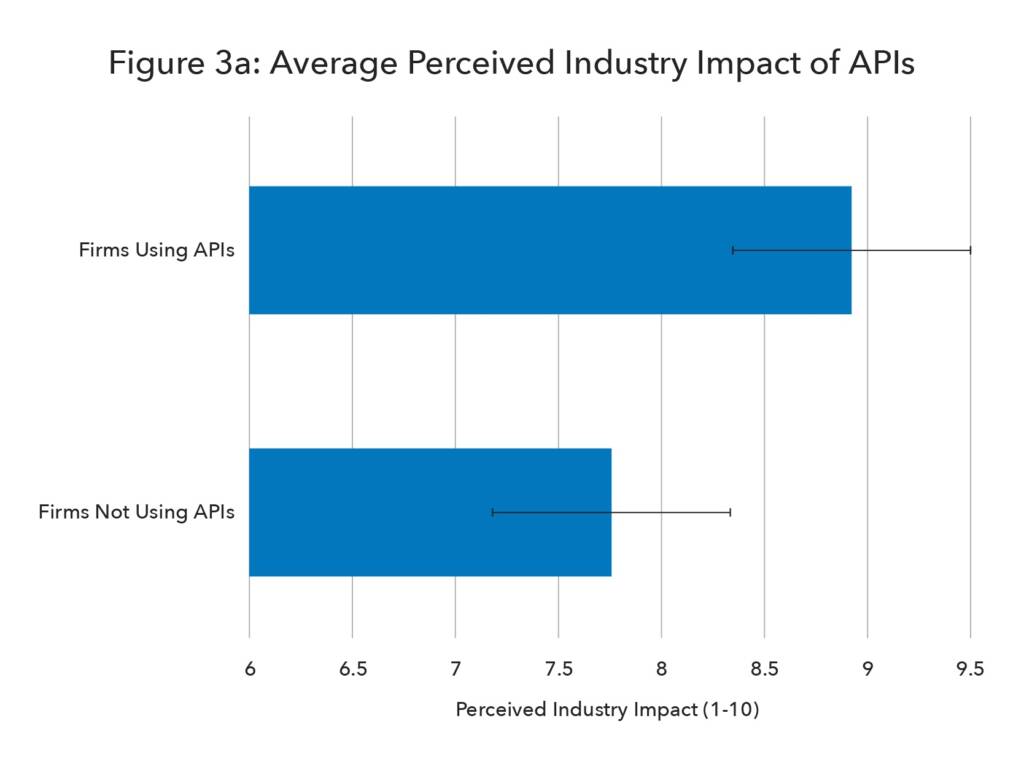
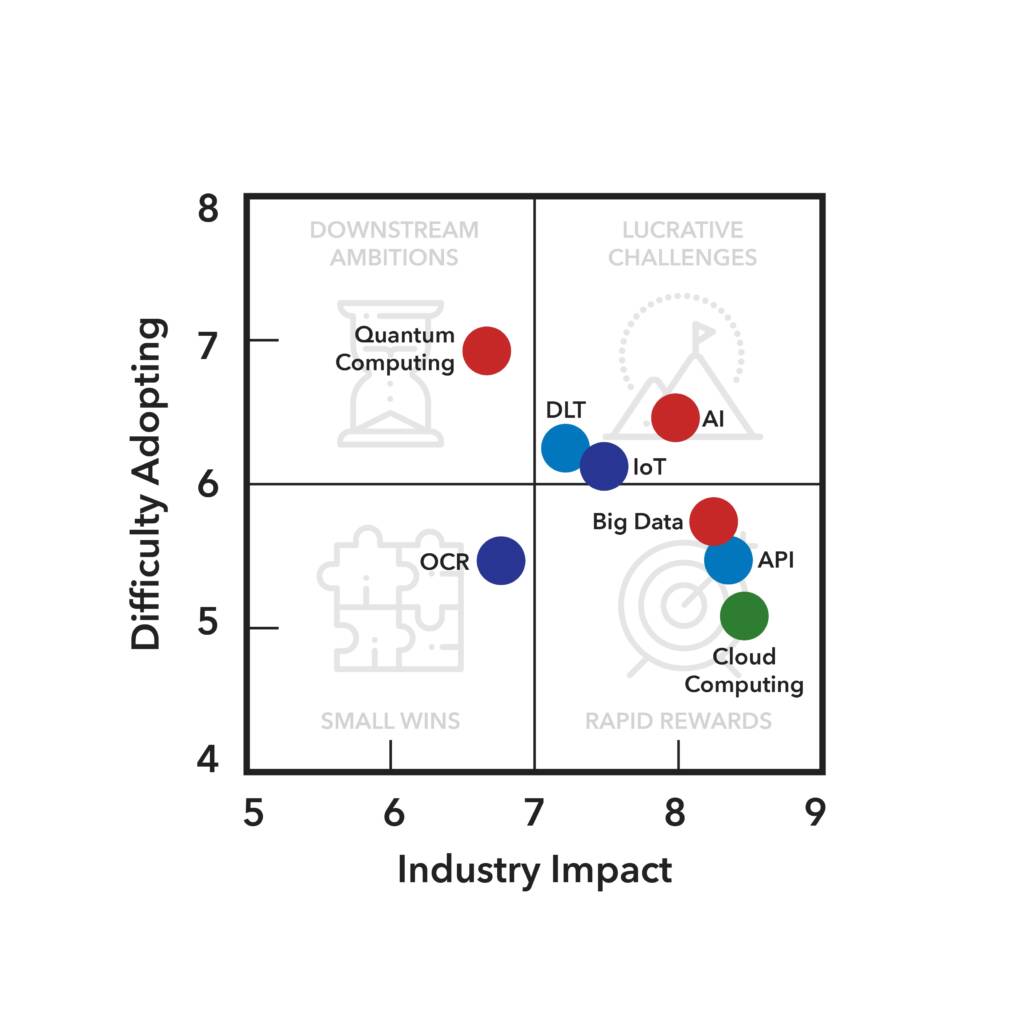
Application Programming Interface
Application programming interface (API) is a software intermediary that effectively allows two applications to interact with each other. APIs define the types of calls or requests that can be made from one application to another, how to make them, the data formats to be used, and the conventions to be followed.
Having been in practical existence since the early 2000s, APIs are widely used and well established in many industries. They are used to connect existing business processes that can aid treasury management, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. APIs are indispensable tools for allowing various applications and software to interconnect and communicate, making it possible to realize the full value of other technologies across different data sources. API development has been touted as a fundamental driver of development work for the internet as a whole.
Potential benefits for MSMEs
In the trade space, the increased development of APIs in recent years has enabled the creation of increasingly customer-centric solutions that solve several significant problems. This can be done by providing customers with instantaneous and transparent access to information about their own orders, transactions, and shipments to which they may not previously have had access. In short, by automating the transfer of data, APIs make platforms more efficient.
Addressing API challenges
Despite being widespread in many industries, APIs come with their own set of challenges, which may affect the efficiency of the solutions being developed to facilitate MSME financing. First is the fact that the costs of developing API connections to external applications are not necessarily a part of firm-level budgets for other software development. This means that the resources to develop these connections need to come from additional budget allocations, which can be difficult to attain. Practitioners in the field have reported difficulties in securing funds to develop APIs as part of their DLT projects to make MSME financing more efficient. Second is the need to have many different APIs: different platforms send different data, creating a need for as many APIs as there are platforms. In addition, any time there is a change in the data structure, the API needs to be changed as well. This issue could be mitigated by the development of standardized data models – a need that is not unique to APIs. The development of standardized data models is, in many respects, a precondition to support the efficient use of digital technologies in trade. Finally, another challenge faced by practitioners in the field is the fact that it is difficult to convince the customer to share the data automatically to provide relevant services. Thought should be given to the development of a common framework on how to leverage data at all stages of the trade technology stack to better assess financing risks and give comfort to customers.
For more information about this diagram, visit our research methodology page.
Featured Insights
 Video | More green, more digital: In conversation with EBRD’s incoming Shona Tatchell and outgoing Rudolf Putz – At the EBRD 2024 annual meeting in Yerevan, Armenia, the Trade Facilitation Program (TFP) was in the spotlight as it transitions leadership from Rudolf Putz to Shona Tatchell.
Video | More green, more digital: In conversation with EBRD’s incoming Shona Tatchell and outgoing Rudolf Putz – At the EBRD 2024 annual meeting in Yerevan, Armenia, the Trade Facilitation Program (TFP) was in the spotlight as it transitions leadership from Rudolf Putz to Shona Tatchell.  VIDEO | Clifford Chance on ETDA: Legal challenges for the new law of the land – To discuss these aspects of the ETDA in detail and shed light on the digital trade transition for the industry, Paul Landless, Partner and Co-Head of the Technology Group, Clifford Chance, joined Deepesh Patel, Editorial Director, Trade Finance Global at the Trade and Investment Forum, organised by BCR in partnership with ITFA.
VIDEO | Clifford Chance on ETDA: Legal challenges for the new law of the land – To discuss these aspects of the ETDA in detail and shed light on the digital trade transition for the industry, Paul Landless, Partner and Co-Head of the Technology Group, Clifford Chance, joined Deepesh Patel, Editorial Director, Trade Finance Global at the Trade and Investment Forum, organised by BCR in partnership with ITFA. VIDEO | Corporate and bank perspective on adopting the ETDA: Use case with Trafigura – Discover the relationship between digitalisation, legislation, and international trade. Explore the impact of the Electronic Trade Documents Act (ETDA) in the UK.
VIDEO | Corporate and bank perspective on adopting the ETDA: Use case with Trafigura – Discover the relationship between digitalisation, legislation, and international trade. Explore the impact of the Electronic Trade Documents Act (ETDA) in the UK.Download our free 2024 publication
TechTrade Finance Hub
1 | TradeTech – Home
2 | The Role of Technology in Trade
3 | Cloud Computing
4 | Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
5 | Internet of Things (IoT)
6 | Application Programming Interfaces (API)
7 | Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
8 | Big Data Analytics
9 | Artificial Intelligence (AI)
10 | Quantum Computing
11 | TradeTech Research
12 | 2021 Whitepaper
13 | ITC AI Guide
 Australia
Australia Hong Kong
Hong Kong Japan
Japan Singapore
Singapore United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates United States
United States France
France Germany
Germany Ireland
Ireland Netherlands
Netherlands United Kingdom
United Kingdom